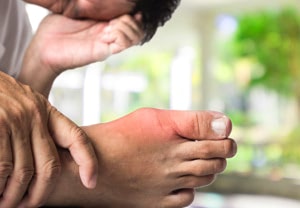
A gout attack can affect different parts of the body.
Gout occurs when excess uric acid is deposited as needle-shaped crystals in tissues or joints of the body. A common symptom of gout is excruciating pain and swelling in the hand joints, often following illness or injury.
Subsequent attacks may occur on and off in other joints, including the wrist and finger joints. If the disease is left untreated for years, lumps of uric acid called tophi may form beneath the skin of the hands.
Signs of a gout attack in your hands are:
- The hand is very painful;
- The hand might be red, swollen and hot to touch;
- The hand might be extremely sensitive to the touch;
- Other symptoms such as fever, headache or weakness may occur.
How long can a gout attack last?
If left untreated, a gout attack can last from 3 days to 2 weeks, until the inflammation reduces and the pain passes. The skin over the affected joint is usually itchy and peels off.
If you suspect you have gout or have had a gout attack, talk to your doctor as soon as possible.
The early diagnosis and treatment of gout make a difference in the course of the disease.