Gout is a lifestyle disease
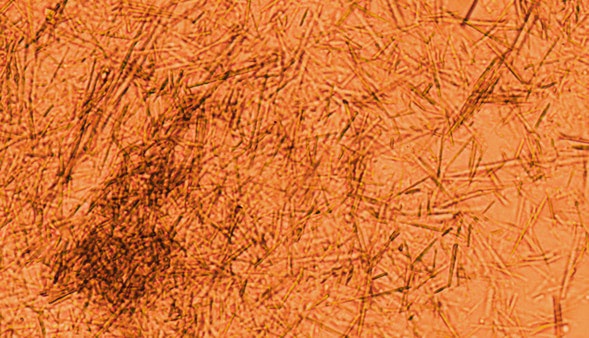
Gout is diagnosed more frequently in industrialised countries and develops as a consequence of increased uric acid levels in the blood (hyperuricaemia) over many years. There are several factors that can raise uric acid levels.
Below 6 mg/dl
Uric acid level: Optimal uric acid level is below 6 mg/dl, or 360 µmol/l.
30 to 60 years
Age: Most patients develop gout between the age of 30 and 60.
80% men
Sex: Men are more frequently affected.
The multisystemic effect of gout on the body
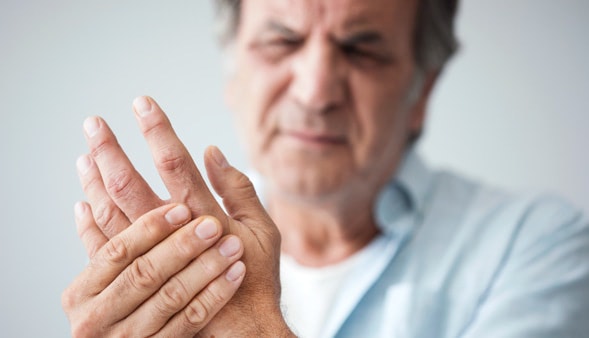
Gout is a multisystemic disease; that means it can affect different parts of the body. Find out more about the impact gout can have on different body parts.
Gout can be treated
Gout is treatable. Acute gout is treated using medication. In order to avoid further gout attacks, a permanent reduction of uric acid levels through lifestyle changes and medication is necessary.