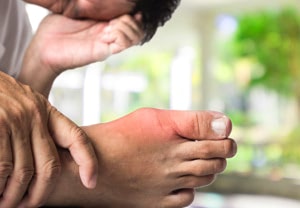
A gout attack can affect different parts of the body.
Gout occurs when excess uric acid is deposited as needle-shaped crystals in tissues or joints. The first symptom of gout is excruciating pain and swelling localised in a specific joint, often following illness or injury. In 80 % of patients, one of the joints in the leg is affected, 60 % of which are the metatarsophalangeal joints – the joints between the bones of the foot and the bones of the toes. The ankle, shoulder or knee joints are less common.
Signs of a gout attack in the foot are:
- The foot is very painful;
- The foot might be red, swollen and hot to touch;
- The foot might be extremely sensitive to the touch;
- Other symptoms such as fever, headache or weakness may occur.
How long can a gout attack last?
If left untreated, a gout attack can last from 3 days to 2 weeks, until the inflammation reduces and the pain passes. The skin over the affected joint is usually itchy and peels off.
If you suspect you have gout or have had a gout attack, talk to your doctor as soon as possible.
The early diagnosis and treatment of gout make a difference in the course of the disease.