Which tests help to diagnose gout?
When your doctor suspects gout, they will use diagnostic tests to confirm the disease in addition to the physical examination. Gout can be diagnosed clinically based on the rapid development of monoarticular arthritis (affecting only one joint), which is usually seen as swelling and redness of the big toe joint. Deposits of uric acid crystals, which form around the joint tissue and are known as "tophi", are also a diagnostic sign of gout.
Blood tests
Elevated uric acid levels and the inflammation stage of the disease can be determined through blood tests.
In a healthy person, the uric acid levels are between 3 and 6 milligrams per 100 millilitres of blood serum. A value of more than 6.5 milligrams per 100 millilitres of blood serum is referred to as hyperuricaemia.
Whilst a blood test cannot fully confirm the diagnosis of gout, uric acid levels are important in determining a diagnosis and measuring a response to uric acid-lowering medicines. Uric acid levels of more than 6 mg/dl, or more than 360 µmol/l, support the diagnosis of gout.
Additionally, inflammation indicators in the blood provide further evidence of gout. These include:
- Increased value of the C-reactive protein;
- Increased white blood cells.
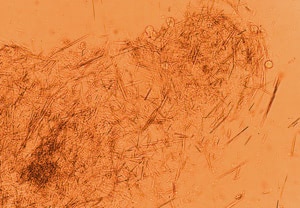
Joint-fluid test
A common means of diagnosing gout is to take a sample of synovial fluid (a fluid which helps to lubricate and protect the joints) from the inflamed joint.
The fluid is examined under a microscope to check for uric acid crystals. If the crystals are present, gout can be diagnosed definitely. Sometimes, taking a sample of synovial fluid is not practical, and the doctor will make a diagnosis of gout based on other factors, including pain patterns, family history of gout and high uric acid levels. The extraction of uric acid crystals from non-inflamed areas can also confirm a gout diagnosis.
Advanced imaging techniques
Imaging techniques like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) using high-resolution multislice scanners and ultrasonography (US) have led to new insights into the diagnosis of gout.